header
header is a sub-structure of Block and UncleBlock, including raw and nonce.
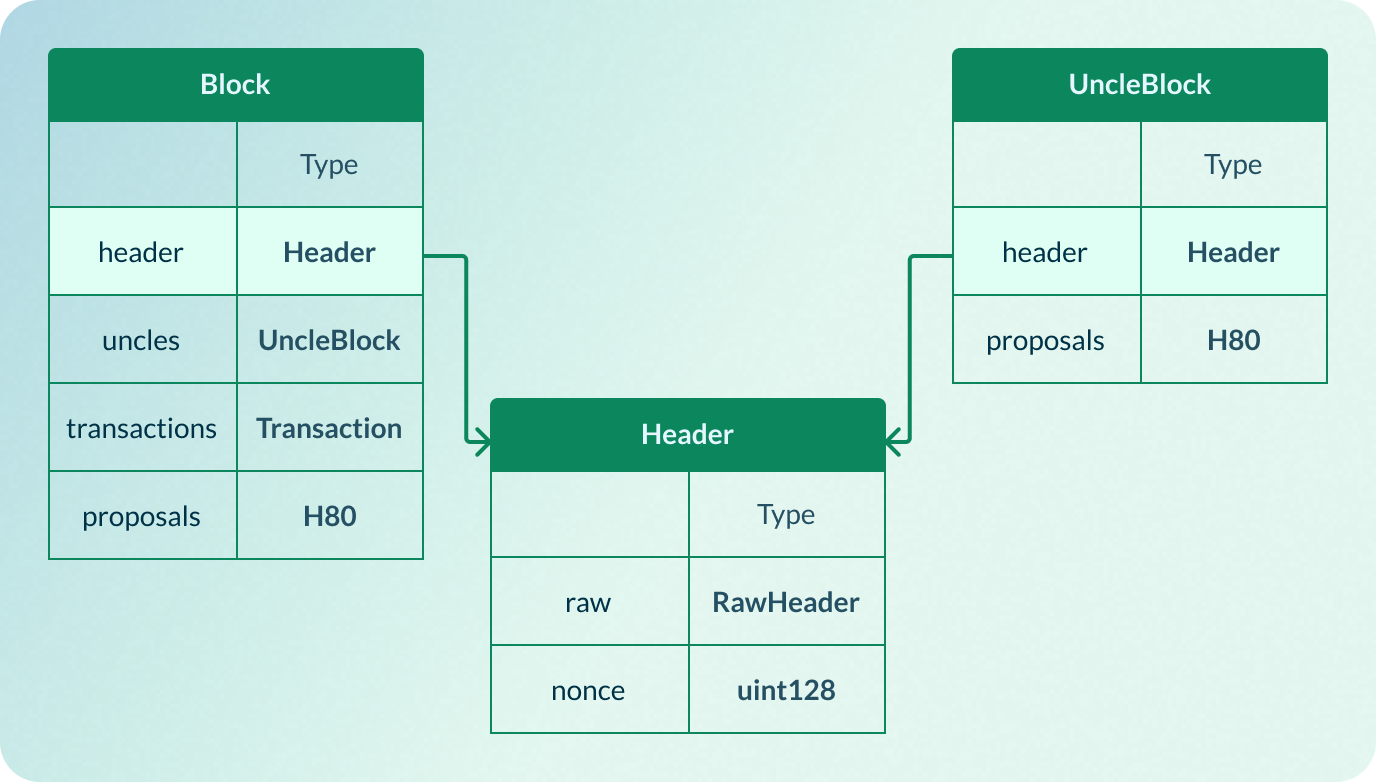
Fields & Description
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
raw | RawHeader | The payload of the block header. For more, see RawHeader. |
nonce | uint128 | The solution of the PoW puzzle. Similar to Bitcoin nonce. |
Verification Process for Header
This following snippet describes the process to validate the PoW for a block header in the Nervos CKB blockchain:
- Serializing and hashing the block's raw data.
- Concatenating the hash with the nonce.
- Running the concatenated result through the Eaglesong algorithm.
- (Optional) Re-hashing for the Testnet.
- Converting the final output to an integer and ensuring it meets the required difficulty target.
pow_hash := ckbhash(molecule_serialize(raw))
pow_message := pow_hash || to_le(nounce)
pow_output := eaglesong(pow_message)
// for Testnet, there is another round of hash
// pow_output = ckbhash(pow_output)
from_be(pow_output) <= compact_to_target(raw.compact_target)
Functions used in the pseudocode
:=: assignment||: binary concatenationckbhash: Blake2b hash with CKB specific configurationto_le: converts unsigned integer to bytes in little-endian. The bytes count is the same with the integer width.from_be: converts bytes encoded in big-endian to an unsigned integermolecule_serialize: serializes a structure into binary using its schemaeaglesong: CKB’s Proof-of-Work consensus algorithm. See RFC0010: Eaglesongcompact_to_target: restores the target from its compact form, which is the difficulty target encoded byraw.compact_target
Header Hash Derivation & Usage
The header is hashed to produce a unique header_hash. This header_hash is then used to reference the block.
header_hash := ckb_hash(molecule_serialize(header))